[자바] java 배열
20. 자료를 순차적으로 한꺼번에 관리하는 방법 - 배열(array)
배열이란?
동일한 자료형의 순차적 자료 구조
인덱스 연산자[]를 이용하여 빠른 참조가 가능
물리적 위치와 논리적 위치가 동일
배열의 순서는 0부터 시작
자바에서는 객체 배열을 구현한 ArrayList를 많이 활용함
배열 선언과 초기화
- 배열 선언하기
int[] arr1 = new int[10]; int arr2[] = new int[10];
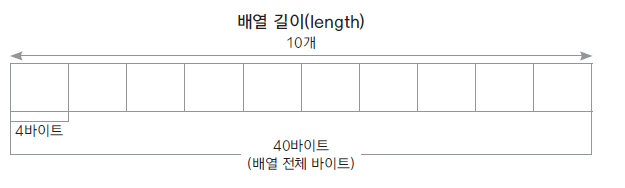
- 배열 초기화 하기
배열은 선언과 동시에 자료형에 따라 초기화 됨 ( 정수는 0, 실수는 0.0, 객체는 null)
필요에 따라 초기값을 지정할 수 있음
int[] numbers = new int[] {10, 20, 30}; //개수 생략해야 함
int[] numbers = {10, 20, 30}; // new int[] 생략 가능
int[] ids;
ids = new int[] {10, 20, 30}; // 선언후 배열을 생성하는 경우는 new int[] 생략할 수 없음
배열 사용하기
[] 인덱스 연산자 활용 - 배열 요소가 저장된 메모리의 위치를 연산하여 찾아 줌
배열을 이용하여 합을 구하기
int[] arr = new int[10];
int total = 0;
for(int i=0, num=1; i< arr.length; i++, num++) {
arr[i] = num;
}
for( int i =0; i<arr.length; i++) {
total += arr[i];
}
System.out.println(total);
배열의 길이와 요소의 개수는 동일하지 않습니다.
배열을 선언하면 개수만큼 메모리가 할당되지만, 실제 요소(데이타)가 없는 경우도 있음
배열의 length 속성은 배열의 개수를 반환해주기 때문에 요소의 개수와는 다름
length를 활용하여 오류가 나는 경우 ``` double[] dArr = new double[5];
dArr[0] = 1.1;
dArr[1] = 2.1; dArr[2] = 3.1;
double mtotal = 1; for(int i = 0; i< dArr.length; i++) { mtotal *= dArr[i]; }
System.out.println(mtotal);
- 요소의 개수에 대한 변수(count)를 따로 유지
double[] dArr = new double[5]; int count = 0; dArr[0] = 1.1; count++; dArr[1] = 2.1; count++; dArr[2] = 3.1; count++;
double mtotal = 1; for(int i = 0; i< count; i++) { mtotal *= dArr[i]; }
System.out.println(mtotal);
## 문자 배열을 만들어 A-Z 까지 배열에 저장하고 이를 다시 출력하기
public class CharArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] alpahbets = new char[26];
char ch = 'A';
for(int i = 0; i<alpahbets.length; i++) {
alpahbets[i] = ch++;
}
for(int i = 0; i<alpahbets.length; i++) {
System.out.println(alpahbets[i] +","+ (int)alpahbets[i]);
}
}
}
## 향상된 for문 사용하기
배열의 n개 요소를 0 부터 n-1까지 순차적으로 순회할 때 간단하게 사용할 수 있음
for( 변수 : 배열) {
}
public class CharArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] alpahbets = new char[26];
char ch = 'A';
for(int i = 0; i<alpahbets.length; i++) {
alpahbets[i] = ch++;
}
for(char alpha : alpahbets) {
System.out.println(alpha +","+ (int)alpha);
}
}
}
-----
# 21. 객체 배열 사용하기
## 객체 배열 선언과 구현
- 기본 자료형 배열은 선언과 동시에 배열의 크기만큼의 메모리가 할당되지만,
객체 배열의 경우엔 요소가 되는 객체의 주소가 들어갈(4바이트, 8바이트) 메모리만 할당되고(null) 각 요소 객체는 생성하여 저장해야 함
예를 들어 person 객체배열 5개를 만들면 person 5개가 생기는 게 아니라 person 5개가 들어갈 주소를 가진 방이 5개가 생긴다고 이해하면 된다.

Book.java
public class Book {
private String title;
private String author;
public Book() {}
public Book(String title, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public void showBookInfo() {
System.out.println(title + "," +author);
} } ```
BookArrayTest.java
public class BookArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] library = new Book[5];
for(int i =0; i<library.length; i++) {
System.out.println(library[i]);
}
}
}
객체를 쓸땐 그냥 new한다고 만들어지는게 아니라 객체를 미리 만들어 둬야 한다.
- 객체를 생성하여 각 배열의 요소로 저장하기
public class BookArrayTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] library = new Book[5];
library[0] = new Book("태백산맥1", "조정래");
library[1] = new Book("태백산맥2", "조정래");
library[2] = new Book("태백산맥3", "조정래");
library[3] = new Book("태백산맥4", "조정래");
library[4] = new Book("태백산맥5", "조정래");
for(int i =0; i<library.length; i++) {
System.out.println(library[i]);
library[i].showBookInfo();
}
}
}
객체 배열 복사하기
System.arrayCopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length) 자바에서 제공되는 배열 복사 메서드
얕은 복사
객체 주소만 복사되어 한쪽 배열의 요소를 수정하면 같이 수정 됨
즉, 두 배열이 같은 객체를 가리킴
public class ObjectCopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book[] library = new Book[5];
Book[] copyLibaray = new Book[5];
library[0] = new Book("태백산맥1", "조정래");
library[1] = new Book("태백산맥2", "조정래");
library[2] = new Book("태백산맥3", "조정래");
library[3] = new Book("태백산맥4", "조정래");
library[4] = new Book("태백산맥5", "조정래");
System.arraycopy(library, 0, copyLibaray, 0, 5);
System.out.println("======copy library=========");
for( Book book : copyLibaray ) {
book.showBookInfo();
}
library[0].setTitle("나목");
library[0].setAuthor("박완서");
System.out.println("======library=========");
for( Book book : library) {
book.showBookInfo();
}
System.out.println("======copy library=========");
for( Book book : copyLibaray) {
book.showBookInfo();
}
}
}
System.arraycopy(library, 0, copyLibaray, 0, 5); 에서 원본의 0부터 복사 하는 곳에 원본의 0부터 5까지 복사해라
깊은 복사
각각의 객체를 생성하여 그 객체의 값을 복사하여 배열이 서로 다른 객체를 가리키도록 함 복사하면 같이 바뀜
public class ObjectCopy2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Book[] library = new Book[5]; Book[] copyLibaray = new Book[5]; library[0] = new Book("태백산맥1", "조정래"); library[1] = new Book("태백산맥2", "조정래"); library[2] = new Book("태백산맥3", "조정래"); library[3] = new Book("태백산맥4", "조정래"); library[4] = new Book("태백산맥5", "조정래"); copyLibaray[0] = new Book(); copyLibaray[1] = new Book(); copyLibaray[2] = new Book(); copyLibaray[3] = new Book(); copyLibaray[4] = new Book(); for(int i = 0; i< library.length; i++) { copyLibaray[i].setTitle(library[i].getTitle()); copyLibaray[i].setAuthor(library[i].getAuthor()); } library[0].setTitle("나목"); library[0].setAuthor("박완서"); System.out.println("======library========="); for( Book book : library) { book.showBookInfo(); } System.out.println("======copy library========="); for( Book book : copyLibaray) { book.showBookInfo(); } } }
객체 복사 쓸떄 같은 객체 가리킬 필요 있으면 굳이 인스턴스 만들면 오버헤드. 근데 인스턴스 값을 복사해서 새로 만들겠다면 객체 복사해서 새로 만들면 됨
22. 2차원 배열 사용하기
다차원 배열
이차원 이상으로 구현 된 배열
평면 (이차원 배열) 이나 공간(삼차원 배열)을 활용한 프로그램 구현
이차원 배열 예제
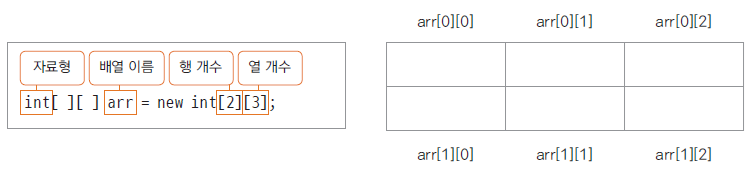
23. 객체 배열을 구현한 클래스 ArrayList
java.util 패키지에서 제공되는 ArrayList
기존의 배열 선언과 사용 방식은 배열의 길이를 정하고 요소의 개수가 배열의 길이보다 커지면 배열을 재할당하고 복사해야 했음
배열의 요소를 추가하거나 삭제하면 다른 요소들의 이동에 대한 구현을 해야 함
ArrayList는 객체 배열을 좀더 효율적으로 관리하기 위해 자바에서 제공해 주는 클래스
이미 많은 메서드들이 최적의 알고리즘으로 구현되어 있어 각 메서드의 사용 방법만 익히면 유용하게 사용할 수 있음
ArrayList의 주요 메서드
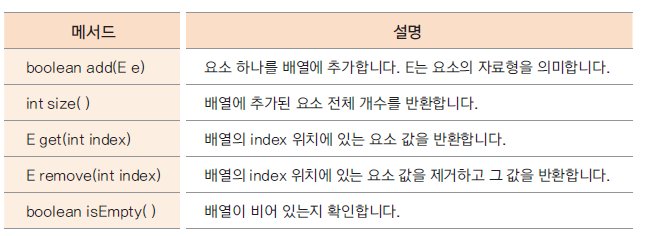
주요 메서드도 잘 봐두자.
ArrayList를 활용한 간단한 예제
import java.util.ArrayList;
import ch21.Book;
public class ArrayListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Book> library = new ArrayList<Book>();
library.add(new Book("태백산맥1", "조정래"));
library.add(new Book("태백산맥2", "조정래"));
library.add(new Book("태백산맥3", "조정래"));
library.add(new Book("태백산맥4", "조정래"));
library.add(new Book("태백산맥5", "조정래"));
for(int i =0; i<library.size(); i++) {
library.get(i).showBookInfo();
}
}
}
24. ArrayList를 활용한 간단한 성적 산출 프로그램
예제 시나리오
1001학번 Lee와 1002학번 Kim, 두 학생이 있습니다.
Lee 학생은 국어와 수학 2과목을 수강했고, Kim 학생은 국어, 수학, 영어 3 과목을 수강하였습니다.
Lee 학생은 국어 100점, 수학 50점입니다.
Kim 학생은 국어 70점, 수학 85점, 영어 100점입니다.
Student와 Subject 클래스를 만들고 ArrayList를 활용하여 두 학생의 과목 성적과 총점을 출력하세요
Student 클래스
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Student {
int studentID;
String studentName;
ArrayList<Subject> subjectList;
public Student(int studentID, String studentName){
this.studentID = studentID;
this.studentName = studentName;
subjectList = new ArrayList<Subject>();
}
public void addSubject(String name, int score){
Subject subject = new Subject();
subject.setName(name);
subject.setScorePoint(score);
subjectList.add(subject);
}
public void showStudentInfo()
{
int total = 0;
for(Subject s : subjectList){
total += s.getScorePoint();
System.out.println("학생 " + studentName + "의 " + s.getName() + " 과목 성적은 " +
s.getScorePoint() + "입니다.");
}
System.out.println("학생 " + studentName + "의 총점은 " + total + " 입니다.");
}
}
Subject 클래스
public class Subject {
private String name;
private int scorePoint;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getScorePoint() {
return scorePoint;
}
public void setScorePoint(int scorePoint) {
this.scorePoint = scorePoint;
}
}
실행하기
public class StudentTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student studentLee = new Student(1001, "Lee");
studentLee.addSubject("국어", 100);
studentLee.addSubject("수학", 50);
Student studentKim = new Student(1002, "Kim");
studentKim.addSubject("국어", 70);
studentKim.addSubject("수학", 85);
studentKim.addSubject("영어", 100);
studentLee.showStudentInfo();
System.out.println("======================================");
studentKim.showStudentInfo();
}
}